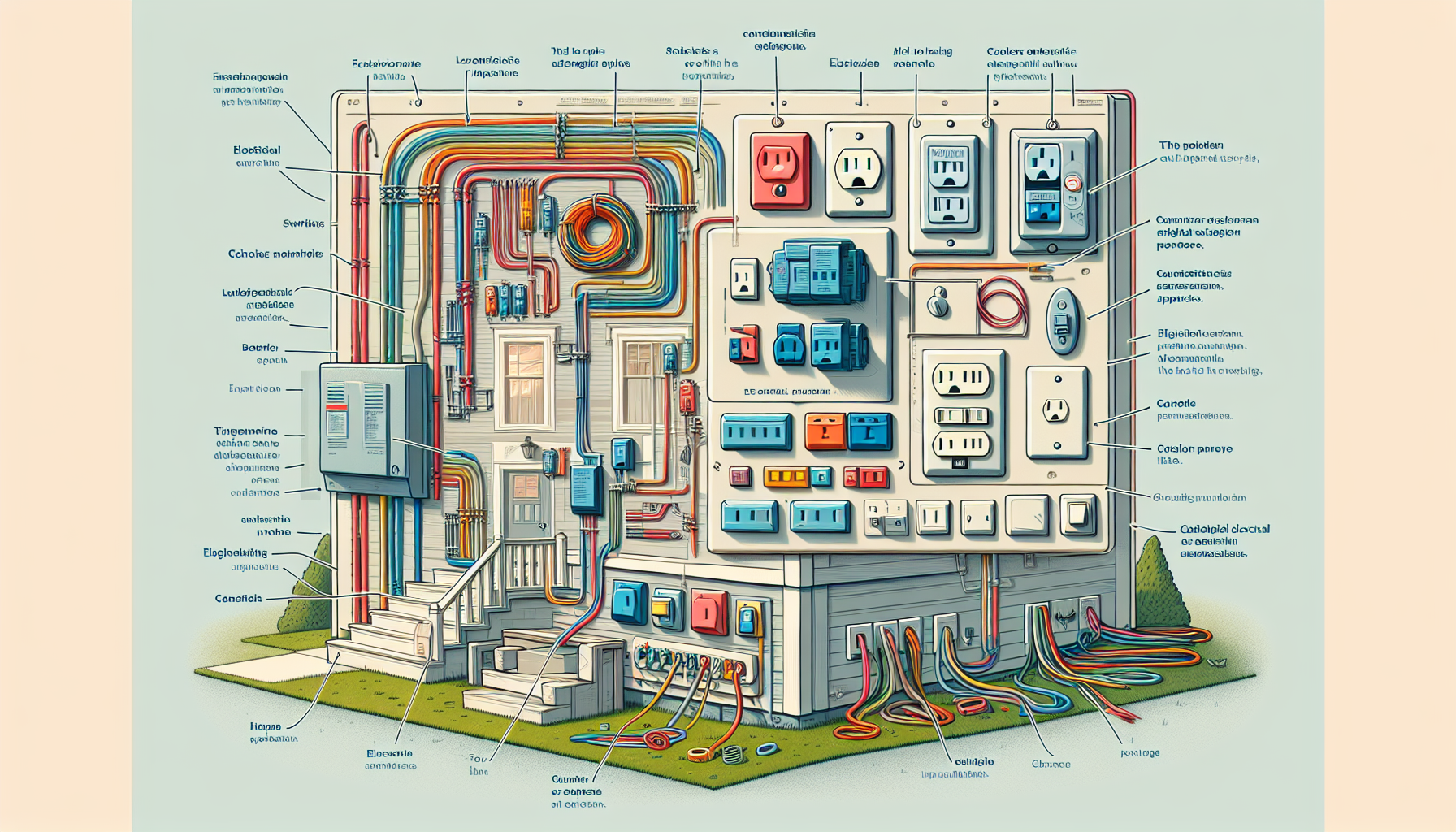
The electrical panel, commonly referred to as the breaker box or fuse box, is the heart of your home’s electrical system. It’s where the electricity from the utility company enters your home and gets distributed to the various circuits that power your lights, appliances, and electronic devices.
Inside the panel, you’ll find a series of switches called circuit breakers, each dedicated to a specific area or type of device in your home. These breakers are safety devices designed to protect your home by automatically shutting off the power if there’s an overload or a short circuit. It’s crucial to know the amperage rating of your panel and ensure that it meets the energy demands of your household to prevent potential hazards.
Navigating the Maze of WiringThe wiring in your home is a complex system of cables running throughout the walls, ceilings, and floors, providing electricity wherever it’s needed. Typically, a home’s wiring includes hot wires (carrying the power), neutral wires (completing the circuit), and ground wires (enhancing safety).
Copper is widely used for wiring due to its excellent conductivity and durability. When examining wiring, gauge size is essential; a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire, which can carry more current. Understanding the type and condition of the wiring is key for both safety and functionality.
Taking Charge of Electrical OutletsElectrical outlets are the points at which you access electricity for plugging in your devices. The most common type you’ll see in your home is the duplex receptacle, which has two plug-ins. These outlets should be grounded (with a third hole for the ground pin on a plug) to reduce the risk of electric shock.
In areas where water is present, such as bathrooms and kitchens, Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are installed. These are designed to cut off power quickly if a ground fault is detected, protecting you from electric shock.
Additionally, with the spread of smart devices and electric vehicles, some homeowners are upgrading to USB outlets and 240-volt outlets to meet their modern electrical needs.
Illuminating the World of SwitchesSwitches come in different styles and functionalities. The most common type of switch found in the home is the single-pole switch, which controls a light or outlet from one location. For greater convenience, three-way switches allow you to control a light or an outlet from two different locations, while four-way switches can control from three or more locations.
Dimmer switches are popular for the control they offer over lighting intensity; they’re perfect for creating ambiance and can even help with energy efficiency. Furthermore, with the rise in home automation, smart switches allow you to control your lights and certain devices remotely via apps or voice commands.
In mastering your home’s electrical system, it’s crucial to recognize the various components that make up the network: the electrical panel is the command center; wiring forms the intricate pathways; outlets are the points of access; and switches grant you the control. Knowing how these elements work together provides a solid foundation for understanding, maintaining, and safely managing the electricity in your home. Whether you’re performing basic maintenance or contemplating upgrades, remember that working with electricity can be dangerous, and when in doubt, always consult with a licensed electrician.







